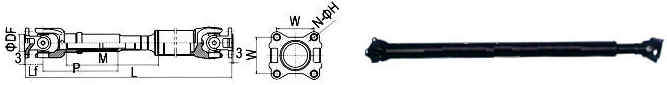
GEAR
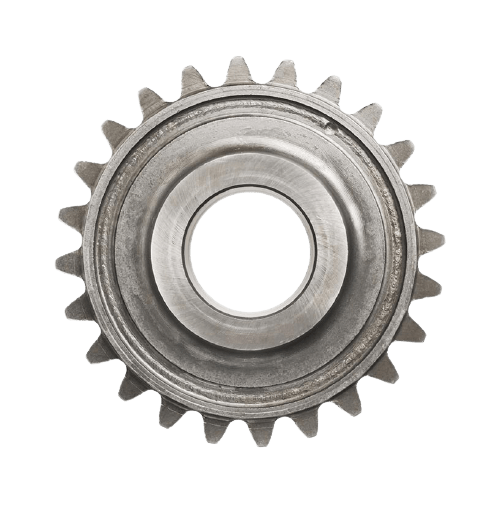

Spur Gears
The most common type of gears employed, spur gears are constructed with straight teeth cut or inserted parallel to the gear’s shaft on a circular (i.e., cylindrical) gear body. In mated pairs, these gears employ the parallel axes configuration to transmit motion and power. Depending on the application, they can be mated with another spur gear, an internal gear (such as in a planetary gear system), or a gear rack (such as in a rack and pinion gear pair).
The simplicity of the spur gear tooth design allows for both a high degree of precision and easier manufacturability. Other characteristics of spur gears include lack of axial load (i.e., the thrust force parallel to the gear shaft), high-speed and high-load handling, and high efficiency rates. Some of the disadvantages of spur gears are the amount of stress experienced by the gear teeth and noise produced during high-speed applications.
This type of gear is used for a wide range of speed ratios in a variety of mechanical applications, such as clocks, pumps, watering systems, power plant machinery, material handling equipment, and clothes washing and drying machines. If necessary for an application, multiple (i.e., more than two) spur gears can be used in a gear train to provide higher gear reduction.

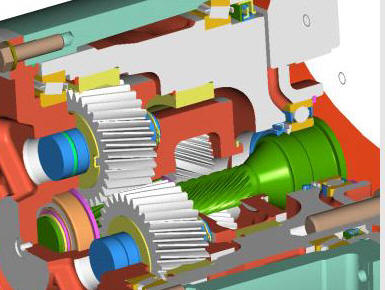
Helical Gears
Similar to spur gears, helical gears typically employ the parallel axes configuration with mated gear pairs, but, if aligned properly, they can also be used to drive non-parallel, non-intersecting shafts. However, unlike spur gears, these gears are constructed with teeth which twist around the cylindrical gear body at an angle to the gear face. Helical gears are produced with right-hand and left-hand angled teeth with each gear pair comprised of a right-hand and left-hand gear of the same helix angle.
The angled design of helical teeth causes them to engage with other gears differently than the straight teeth of spur gears. As properly matched helical gears come in contact with one another, the level of contact between corresponding teeth increases gradually, rather than engaging the entire tooth at once. This gradual engagement allows for less impact loading on the gear teeth and smoother, quieter operation. Helical gears are also capable of greater load capabilities but operate with less efficiency than spur gears. Further disadvantages include the complexity of the helical tooth design, which increases the degree of difficulty in its manufacturing (and, consequently, the cost) and the fact that the single helical gear tooth design produces axial thrust, which necessitates the employment of thrust bearings in any application which uses single helical gears. This latter necessity further increases the total cost of using helical gears.
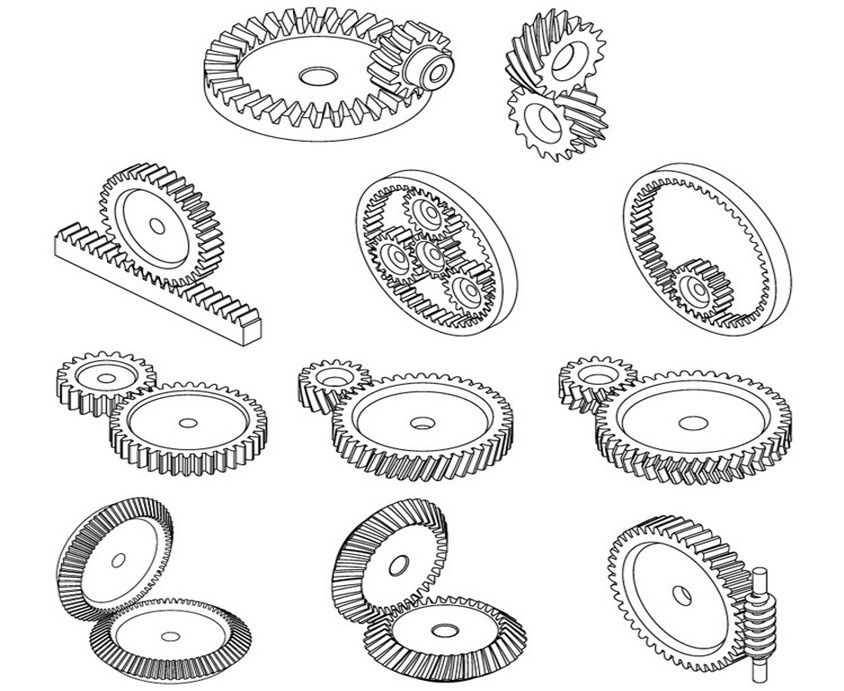
|
Type of Gear |
Characteristics |
|
Spur |
|
|
Helical |
|
|
Bevel |
|
|
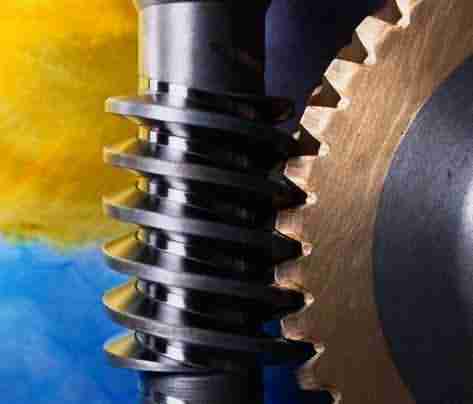
Worm |
|
|
Rack and Pinion |
|
Bevel Gears
Bevel gears are cone-shaped gears with teeth placed along the conical surface. These gears are used to transmit motion and power between intersecting shafts in applications which require changes to the axis of rotation. Typically, bevel gears are employed for shaft configurations placed at 90-degree angles, but configurations with lesser or greater angles are also manageable.
There are several types of bevel gears available differentiated mainly by their tooth design. Some of the more common types of bevel gears include straight, spiral, and hzpt bevel gears.
Straight Bevel Gears
The most commonly used of the bevel gear tooth designs due to its simplicity and, consequently, its ease of manufacturing, straight bevel teeth are designed such that when properly matched straight bevel gears come into contact with one another, their teeth engage together all at once rather than gradually. As is the issue with spur gears, the engagement of straight bevel gear teeth results in high impact, increasing the level of noise produced and amount of stress experienced by the gear teeth, as well as reducing their durability and lifespan.
Spiral Bevel Gears
In spiral bevel gears, the teeth are angled and curved to provide for more gradual tooth engagement and more tooth-to-tooth contact than with a straight bevel gear. This design greatly reduces the vibration and noise produced, especially at high angular velocities (>1,000 rpm). Like helical gears, spiral bevel gears are available with right-hand or left-hand angled teeth. As is also the case with helical gears, these gears are more complex and difficult to manufacture (and, consequently, more expensive), but offer greater tooth strength, smoother operation, and lower levels of noise during operation than straight bevel gears.
Why choose us?
(1) We provide OEM services and submit various styles and latest designs to customers;
(2) We cooperate with major customers in Southeast Asia, Africa, the Middle East, North America and South America;
(3) According to the needs of customers in different regions, we have matched various styles of reducers for you, so that our customers have great competitiveness in the market!
(4) We have more than 20 years of rich experience in providing customers with high-quality products and the most professional services!
(5) We can flexibly export goods from any port in China! You are welcome to inquire!
company advantage:
1. Large production capacity and fast delivery.
2. Strict quality control inspection rules: all products must pass 100% inspection before delivery.
3. Provide OEM/ODM service
4. 24-hour online service.
5. Real-time quotation query
6. High quality, high reliability and long product life.
7. Professional manufacturers provide competitive prices.
8. Diversified, experienced skilled workers.
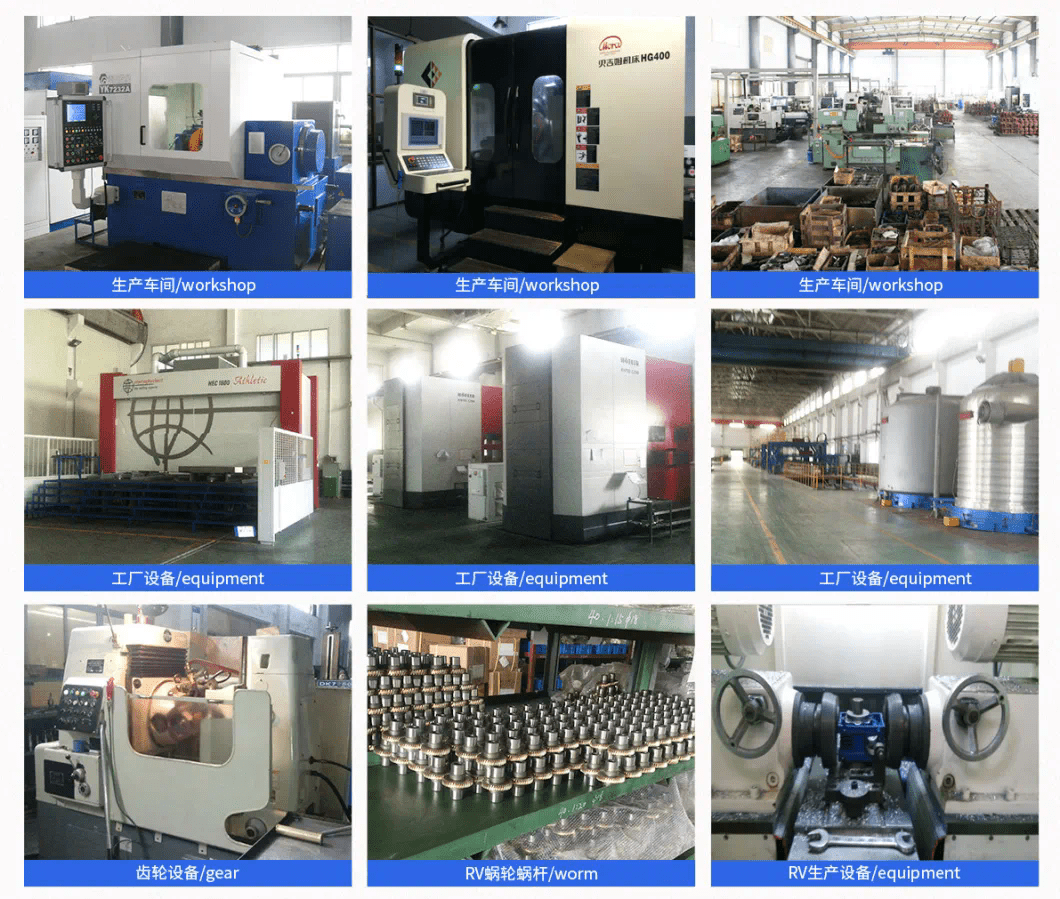

Quality management system:
In HZPT, product and service quality is given the highest priority.
Our employees receive training on quality methods and principles.
At every level of the organization, we are committed to improving product quality and processes.
Such a deep commitment has helped us attract the trust of customers and become the world’s preferred brand.
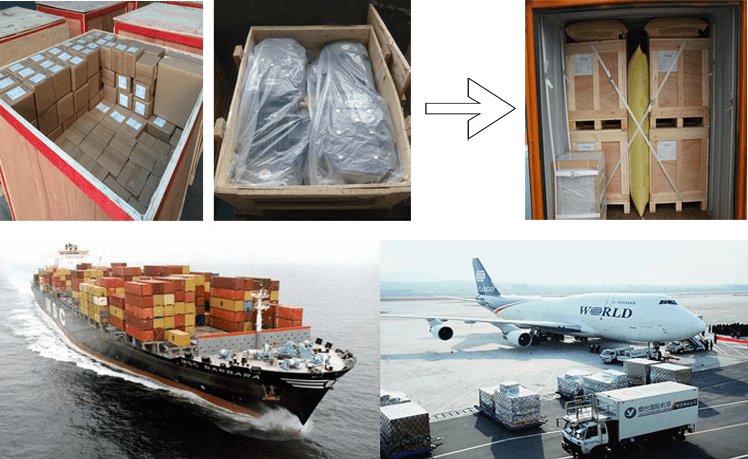
Package & Lead Time
Size: Drawings
Wooden Case/Container and pallet, or as per customized specifications.
15-25days samples. 30-45days offcial order
Port: Shanghai/Ningbo port
FAQ’s
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
To The Client’s
Is purchasing from China profitable?
China remains ones of the biggest supplier in the world. For sure the products that you have chosen is profitable in your target markets, as China is supplying to the world with competitive quality and prices.
2) Do I need to travel China in order to purchase products?
We take care of everything for you, so you can save air fare costs, hotels and traveling expenses. However, if you decide to visit China, we will try to arrange you a wonderful staying so your traveling experience will be pleasant.
3) What type of products do you supply?
A wide range of Industrial, Automotive and Agriculture products. Every product is assigned to a specialized team.
4) What are my risks in buying from China or to work with you?
You have basically no risks. We do purchasing for you and you can rest assure with our inspections. If you get time to come China, you can visit us during production process. You have access to our contact networks and sales team. We will take serious action about your products like ours. You do not need to travel if you don’t want to as you have knowledgeable partners in the China.
5) I can find the supplier for my products on my own, why do I need you?
You may do so. However, your investment will be much higher. Plus you do not have a local partner that knows the market and can give you access to a network of opportunity.
To buy your products from China, you need to have a local office for signing contract with suppliers, an engineer team in order to do quality and quantity inspection time to time. You need to know about raw material sources, and the important matter is to avoid any out sourcing.
6) How are you structured?
We have different departments that each one specialized in every single aspect. We can provide logistic assistance, Sourcing assistance, inspection assistance, and legal assistance.
7) Is this service only for large corporation?
No, we sure that by first time corporation you will get warm confidence to keep your business with us, as our relationship based on honesty and mutual benefits, so in the future you will enlarge your business. We care you and make you to be much more-stronger than before. Going from strength to strength together.
We welcome any corporation from Small to Large, Let’s progress . . .
For more queries please send us email



/helica1.jpg)